export Barberry
CATALOGUE
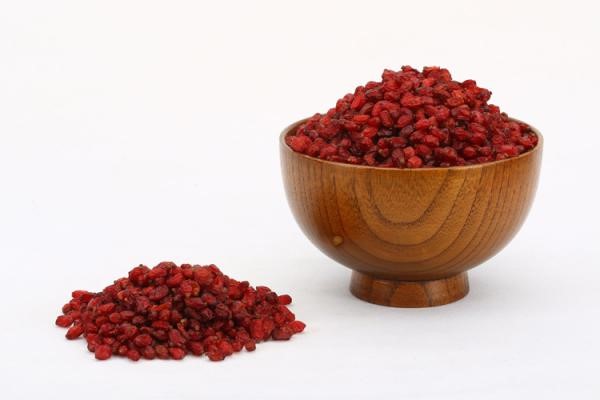
Barberry bushes have a sweet-sour flavor with a nice, pleasant taste that is often compared to some other berry family members such as cranberries. The dried barberry grows on the bush and is commonly used in Persian and Ottoman cooking within rice cuisines due to its beautiful jewel-like appearance and pleasant taste. This is also used to make sweet, tart jams and juices and a lot more other places. Barberries are long red berries that grow on barberry shrubs, which have branches covered in yellow flowers. Known as zereshk in Iran, barberries have long been part of traditional medicine. The small berries contain alkaloid berberine, which can cause adverse effects in large amounts.
Barberry can grow to be a fairly large shrub. The thorny shoots are found growing wild in Alborz mountains amplitudes and other parts of Iran. Ruby is the name given to seedless barberry which is cultivated in Qaenat and emerges from an erect shrub of 1.5-2 meters tall.
History of barberry
Barberry is a bush native to Europe, North Africa that now grows wild in many regions of North America. The berries of the barberry are traditionally used to make jams and jellies. But the herb also has a long history as a folk remedy for digestive disorders, including constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, heartburn, and loss of appetite.
It was traditionally thought to increase the flow of bile, which is why it was used for liver and gallbladder problems. It was also used topically to treat skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, acne, and minor wounds.
What Do dried Barberries Taste Like?
European barberries have a tart flavor, similar to cranberries, while barberries from North America are sweeter. European barberries typically aren’t eaten raw without some kind of flavoring, since they can be intensely sour. When cooked or dried, the mellowed sourness of barberries complements everything from meat dishes to granola.

4 Common Types of Barberry
There are about 500 plants in the Burseraceae family, all of which produce a tart, edible berries. Some of the most common barberry plants include:
- European barberry(Berberis vulgaris) is the most common barberry variety and the one you’ll find in Middle Eastern cuisine.
- Japanese barberry(Berberis thunbergii) is most commonly planted as an ornamental.
- American barberry(Berberis canadensis) is native to North America.
- Oregon grape(Mahonia aquifolium), also known as the holly grape, is native to the Pacific Northwest.
Barberry Nutrition facts
-
Calories: 89
-
Protein: 1 grams
-
Fiber: 3 grams
-
Carbohydrates: 18 grams
-
Fat: 1 grams
dried barberry Wholesale
South Khorasan, a province of Iran, is the barberry land, Barberries Zereshk premium quality wholesale available, barberry type is puffy barberry and Anari barberry, Barberry, Zereshk, at Wholesale Price. Berberis Vulgaris also known as common barberry is mostly is recognized as Zereshk.
Sepcotrading company exports the best kind of Iranian dried fruits and nuts like barberries at the most affordable prices all around the world. Click the following button now.
Contact Now
Barberry Health Benefits
Evidence for any health benefits from barberry is extremely weak, though there are studies of berberine that may apply to barberry. Any benefit from barberry likely relies on the fact that it contains berberine, for which medical uses are being established.
There is little scientific evidence supporting the medicinal use of barberry, but there is some evidence to support the use of berberine. Berberine is a chemical compound found in several plants, including barberry.
Diabetes
Berberine seems to slightly reduce blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. The results of one pilot study on 84 patients published in 2008 suggest that taking 500 mg of berberine two to three times a day for up to three months might control blood sugar as effectively as metformin, the first-line drug for type 2 diabetes.
In addition, berberine showed a favorable influence on cholesterol, unlike metformin, which has barely any effect. As the authors of a review article from 2015 noted, “with little documentation of adverse effects, berberine is positioned as a potential candidate drug to treat type 2 diabetes.”
High Cholesterol
There is early evidence that berberine can help lower cholesterol levels in people with high cholesterol. Taking 500 mg of berberine twice a day for three months seems to reduce total cholesterol, LDL or “bad” cholesterol, and triglyceride levels in people with high cholesterol.
High Blood Pressure
Taking 0.9 grams of berberine a day along with the blood pressure-lowering drug amlodipine reduces systolic blood pressure (the top number) and diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number) better than taking amlodipine alone in people with high blood pressure.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Research suggests that berberine can lower blood sugar, improve cholesterol and triglyceride levels, reduce testosterone levels, and lower waist-to-hip ratio in women with PCOS, a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. In some women with PCOS, the drug metformin is prescribed to prevent diabetes from developing (women with PCOS have been shown to have higher levels of insulin when compared to women of the same weight without the condition).
Diarrhea
One of the most well-known uses for barberry was as an herb for treating diarrhea and dysentery, and research for this purpose goes back at least as far as the middle of the 20th century.
8 Impressive Health Benefits of Barberries
- Barberries are highly nutritious.
- Contain beneficial plant compounds.
- May help manage diabetes.
- Can help treat diarrhea.
- May protect against metabolic syndrome.
- Good for dental health.
- May have anticancer effects.
- May help fight acne.
FAQ
Barberries are a small berry that, in their dried form, are prominent in Persian cuisine. They resemble a currant or a dried cranberry, as you can see here. Barberries have a distinctive taste that starts sweet but ends on a very tart note.
People using normal and appropriate doses of barberry do not generally report side effects. Cases of nosebleeds and vomiting have been reported with extremely high doses of this herb. In infants, berberine (a constituent of barberry) may interfere with liver function and might worsen jaundice.
Berberine is a chemical found in several plants including European barberry, goldenseal, goldthread, greater celandine. Berberine is most commonly taken for diabetes, high levels of cholesterol or other fats in the blood and high blood pressure.
Research shows that berberine can lower blood sugar, improve cholesterol and triglyceride levels, reduce testosterone levels, and lower waist-to-hip ratio in women with PCOS. Berberine may even lower blood sugar levels similarly to metformin and may improve cholesterol levels better than metformin.
A common dosage recommendation is 500 mg, 3 times per day, half an hour before meals. Berberine may cause digestive side effects in some people.
Berberis vulgaris, commonly known as barberry, is a shrub that grows tart, red berries. Its berries have been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat digestive issues, infections, and skin conditions.
In Ayurveda, it is traditionally used to cure various infections of eye, ear and mouth, to lose weight, to heal wounds quickly, to cure piles and hemorrhoids, to treat dysentery, indigestion, uterine and vaginal disorders as well as to treat snake or Scorpion bite as an antidote.